 |
R Software |
 |
|---|
This page provides brief descriptions of R packages related to my work on data visualization and the history of statistical graphics. More up-to-date details can be found on my GitHub packages page.
 "
"
heplots: Visualizing multivariate hypothesis tests
 The heplots package provides functions for visualizing
hypothesis tests in multivariate linear models. They represent
sums-of-squares-and-products matrices for linear hypotheses and
for error using ellipses (in two dimensions) and ellipsoids (in
three dimensions). See
Fox, Friendly and Monette (2009) for a
brief introduction.
The heplots package provides functions for visualizing
hypothesis tests in multivariate linear models. They represent
sums-of-squares-and-products matrices for linear hypotheses and
for error using ellipses (in two dimensions) and ellipsoids (in
three dimensions). See
Fox, Friendly and Monette (2009) for a
brief introduction.
Links
- heplots package on CRAN
- heplots GitHub repo
- Pkgdown documentation
- HE Plots for Multivariate Linear Models (JCGS paper)
- HE plots for Repeated Measures Designs (JSS paper)
candisc: Generalized canonical discrimininant analysis
The candisc package includes functions for computing and visualizing generalized canonical discriminant analyses for a multivariate linear model (mlm). They are designed to provide low-rank visualizations of terms in a mlm via the plot method and the heplots package.

Links
vcd and vcdExtra: Visualizing Categorical Data
 The vcd package, by David Meyer, Achim Zeileis, Kurt Hornik provides a fully-general
implementation of the graphical methods for categorical data analysis described
in my book, Visualizing Categorical Data.
In particular, mosaic plots, association plots, sieve diagrams and related methods
are implemented in a common, general framework of the "strucplot".
The vcd package, by David Meyer, Achim Zeileis, Kurt Hornik provides a fully-general
implementation of the graphical methods for categorical data analysis described
in my book, Visualizing Categorical Data.
In particular, mosaic plots, association plots, sieve diagrams and related methods
are implemented in a common, general framework of the "strucplot".
The vcdExtra package extends these methods in a variety of
ways. In particular, vcdExtra extends mosaic, assoc and sieve plots from vcd to
handle glm() and gnm() models and adds a 3D version in mosaic3d().
Links
- vcd package on CRAN
- vcdExtra package on CRAN
- Journal of Statistical Software article,
The strucplot framework: Visualizing multi-way contingency tables with vcd.
[
vignette("strucplot", package="vcd")] -
Tutorial: Working with categorical data with R and the vcd package
[
vignette("vcd-tutorial", package="vcdExtra")]
genridge: Generalized ridge trace plots for ridge regression
 The genridge package introduces
generalizations of the standard univariate ridge trace plot used in ridge regression and related methods. These
graphical displays show both bias and precision, by plotting covariance ellipsoids of the estimated coefficients,
rather than just the estimates themselves.
The genridge package introduces
generalizations of the standard univariate ridge trace plot used in ridge regression and related methods. These
graphical displays show both bias and precision, by plotting covariance ellipsoids of the estimated coefficients,
rather than just the estimates themselves.
Links
- genridge package on CRAN
- Pkgdown documentation
- genridge GitHub repo
- The Generalized Ridge Trace Plot: Visualizing Bias and Precision (JCGS paper)
mvinfluence: Influence measures and diagnostic plots for multivariate linear models
 The mvinfluence package calculates
regression deletion diagnostics for multivariate linear models that are close analogs of methods for univariate and generalized
linear models. Some new plotting methods are included, among these, the LR plot of generalized leverage and residuals.
The mvinfluence package calculates
regression deletion diagnostics for multivariate linear models that are close analogs of methods for univariate and generalized
linear models. Some new plotting methods are included, among these, the LR plot of generalized leverage and residuals.
Links
Guerry: maps, data and methods related to Guerry's Moral Statistics of France
 The Guerry package comprises maps of France in 1830,
data from Andre-Michel Guerry and others,
and statistical and graphic methods related to Guerry's Moral Statistics of France (1833).
The goal of providing these as an R package is to facilitate the exploration and development of
statistical and graphic methods for multivariate data in a geo-spatial context.
The Guerry package comprises maps of France in 1830,
data from Andre-Michel Guerry and others,
and statistical and graphic methods related to Guerry's Moral Statistics of France (1833).
The goal of providing these as an R package is to facilitate the exploration and development of
statistical and graphic methods for multivariate data in a geo-spatial context.
The package contains a vignette,
Spatial multivariate analysis of Guerry's data in R [vignette("MultiSpat")] by Stéphane Dray,
demonstrating both classical approaches and modern methods that attempt to integrate geographical and
multivariate aspects simultaneously.
Links
- Guerry package on CRAN
- A.-M. Guerry's Moral Statistics of France: Challenges for Multivariable Spatial Analysis (Statistical Science paper)
- Spatial multivariate analysis of Guerry's data in R (Guerry vignette)
HistData: Historical Data Sets
 The HistData package provides a collection of data sets that are interesting and important
in the history of statistics and data visualization.
The goal of the package is to make these available,
both for instructional use and for historical research.
The HistData package provides a collection of data sets that are interesting and important
in the history of statistics and data visualization.
The goal of the package is to make these available,
both for instructional use and for historical research.
Some of the data sets have examples which reproduce an historical graph or analysis.
These are meant mainly as starters for more extensive re-analysis or graphical elaboration.
Some of these present graphical challenges to reproduce in R.
Links
Lahman: Lahman Baseball Data Archive
 The Lahman package is an R version of
the Lahman Baseball Data Archive.
This database contains pitching, hitting, and fielding statistics for Major League Baseball from 1871 through 2014.
As an R package, it offers a variety of interesting challenges and opportunities for data processing and visualization in R.
The Lahman package is an R version of
the Lahman Baseball Data Archive.
This database contains pitching, hitting, and fielding statistics for Major League Baseball from 1871 through 2014.
As an R package, it offers a variety of interesting challenges and opportunities for data processing and visualization in R.
Links
- Lahman package on CRAN
- Pkgdown documentation
- Lahman project on GitHub with further information and examples
tableplot: Semi-graphic tabular displays
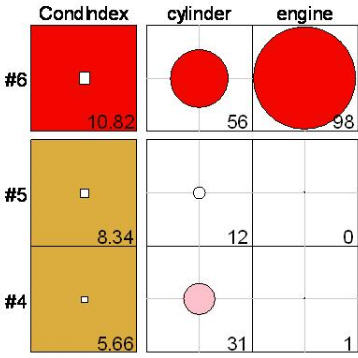 A tableplot (developed by Ernest Kwan) is a semi-graphic display in the form of a table with numeric values, supplemented by symbols with size proportional to cell value(s),
and with visual attributes that can be used to encode other information.
The tableplot package
provides an implementation.
A tableplot (developed by Ernest Kwan) is a semi-graphic display in the form of a table with numeric values, supplemented by symbols with size proportional to cell value(s),
and with visual attributes that can be used to encode other information.
The tableplot package
provides an implementation.
Links
- tableplot package on CRAN
- Tableplot: A New Tool for Assessing Precise Predictions Zeitschrift/Journal of Psychology article
- Visualizing Collinearity Diagnostics: Where's Waldo? TAS paper
WordPools: Word lists for psychology experiments
An R package collecting several classical word pools used in studies of learning and memory (Paivio word list, Toronto Word Pool, Battig and Montague categorized words) and functions for selecting word lists with given ranges on variables.
- WordPools package on CRAN
- Pkgdown documentation
- See also: Online Word Generator for the Paivio word list.
Other R packages
Some links to a few important R packages for data visualization and statistical analysis
- car: John Fox's package for Companion to Applied Regression, provides a wide variety of graphical methods for a wide variety of linear and generalized linear models, and analysis methods for multivariate linear models.
- effects: John Fox's package for effect plots for linear and generalized linear models, provides a simple way to visualize the effects for any term or terms in complex models.

